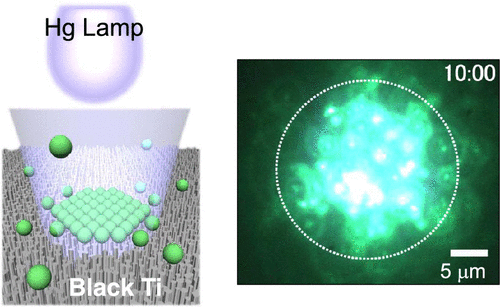
[インコヒーレント光を用いた光捕捉法]
従来の光ピンセットには高強度のレーザー光(コヒーレント光)が必要不可欠ですが、チタンナノ構造体(ブラックチタン)を用いることで、高圧水銀ランプ(インコヒーレント光)でも水溶液中のナノ粒子を捕集できることを発見しました。
坪井教授(大阪市立大学)、鳥本教授(名古屋大学)、Ivanova教授(RMIT大学)、Juodkazis教授(Swinburne工科大学)らのグループとの共同研究の成果です。
- 研究成果のポイント
- 波長370 nmの微弱な紫外光(通常の光ピンセットの106分の1スケール)をブラックチタン表面に照射すると、溶液中のポリスチレンナノ粒子(直径20-500nm)を光捕捉することに成功
- 波長 480,546,580 nmのインコヒーレント光では捕捉できず、紫外光がこの高効率な光捕捉に必要不可欠であることを実証
- ブラックチタン表面にある不動態のTiO2層が重要な役割を担っている可能性があることを電磁場シミュレーションの結果と併せて示唆した。
- Incoherent Optical Tweezers on Black Titanium
- Sayaka Hashimoto, Yuki Uenobo, Ryota Takao, Ken-ichi Yuyama, Tatsuya Shoji, Denver P. Linklater, Elena Ivanova, Saulius Juodkazis, Tatsuya Kameyama, Tsukasa Torimoto, Yasuyuki Tsuboi*
- ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 13 (2021), 27586-27593.
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.1c04929
Optical tweezers enable the manipulation of micro- and nanodielectric particles through entrapment using a tightly focused laser. Generally, optical trapping of submicron size particles requires high-intensity light in the order of MW/cm2. Here, we demonstrate a technique of stable optical trapping of submicron polymeric beads on nanostructured titanium surfaces (black-Ti) without the use of lasers. Fluorescent polystyrene beads with a diameter d = 20–500 nm were successfully trapped on black-Ti by low-intensity focused illumination of incoherent light at λ = 370 m from a Hg lamp. Light intensity was 5.5 W/cm2, corresponding to a reduced light intensity of 6 orders of magnitude. Upon switching off illumination, trapped particles were released from the illuminated area, indicating that trapping was optically driven and reversible. Such trapping behavior was not observed on nonstructured Ti surfaces or on nanostructured silicon surfaces. Thus, the Ti nanostructures were demonstrated to play a key role.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.1c04929